
Ad-hoc reports also can include requests for drill-down reports, key-indicator reports and comparative reports. Routine reports are produced at scheduled intervals. The information is provided in a variety of reports (routine, ad hoc and exception) and provide information to managers regardless of their functional areas. They use this information to help them plan, organize, and control operations. What is a functional area information system? List its major characteristics.įunctional area information systems (FAISs) provide information mainly to lower and middle-level managers in the functional areas. The backbone of most information systems applications is the transaction processing system.ġ. TPSs have to handle high volume and large variations in volume efficiently, avoid errors and downtime, record results accurately and securely, and maintain privacy and security. These data are inputs to the organization’s database. Transaction processing (TPSs) monitor, collect, store, and process data generated from all business transactions. What is a Transactional Processing and the role of TP systems. These tasks in real time by means of online technologies.1. Unit, and increasing the store’s cash position by the amount you paid. Sale by reducing the inventory on hand by one unit, increasing sales figures for the item by one

For example, when you pay for an item at a store, the system records the In online transaction processing (OLTP), business transactions are processed online as The system then prepares and processes the batches periodically In batch processing, the firm collects data from transactions as they occur, placing Next, the system processes data in one of two basic ways: batch processing and online processing.
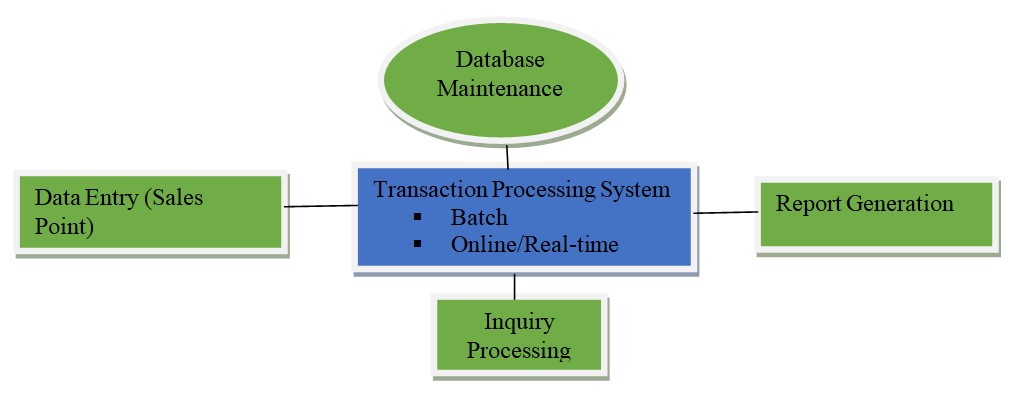
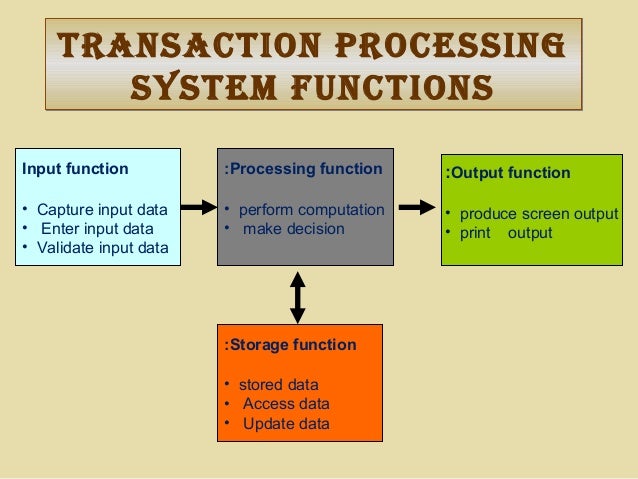
Much as possible because of the large volume involved, a process called source data automation. Generally speaking, organizations try to automate the TPS data entry as As theįirst step in this procedure, people or sensors collect data, which are entered into the computer Whether it occurs in a manufacturing firm, a service firm, or a government organization. Regardless of the specific data processed by a TPS, the actual process tends to be standard, In fact, for certain transactions an audit
In an organization a transaction processing system update#
In addition, the store must update its inventory. ForĮxample, if you return a sweater that you have purchased, the store must credit your creditĬard for the amount of the purchase, refund your cash, or offer you an in-store credit to It is also necessary to reverse a transaction when a purchased item is returned.
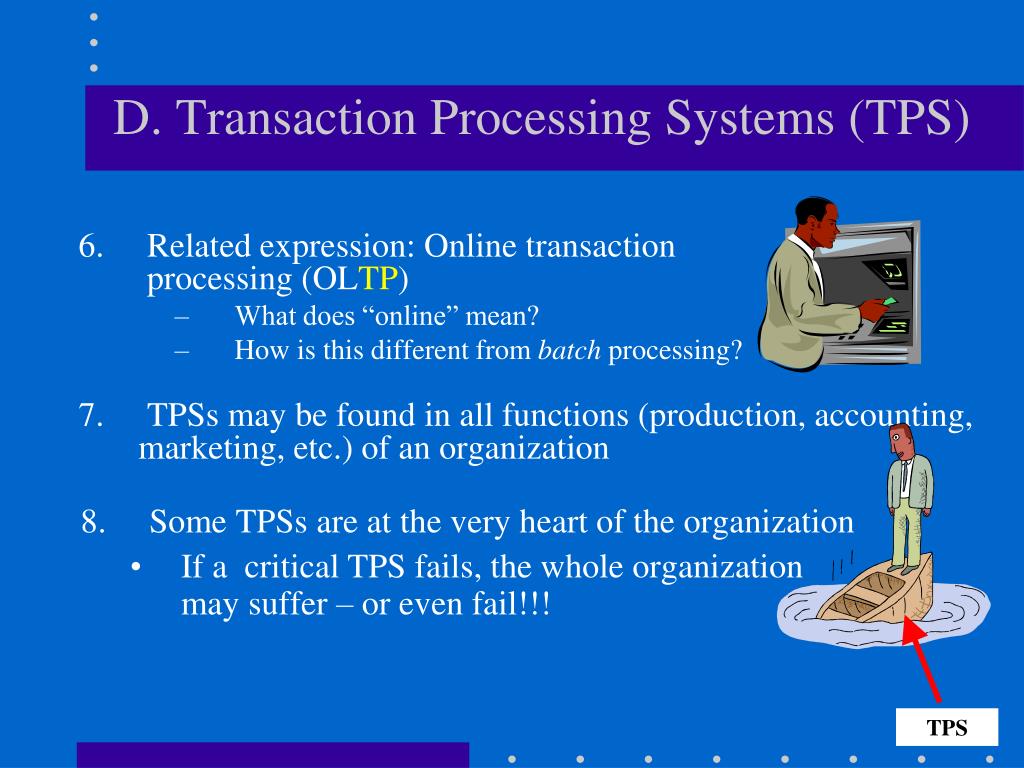
Generated-and it provides the input data for the corporate databases. The TPS collects data continuously, typically in real time-that is, as soon as the data are Processing of data from the organization’s basic business transactions, each of which generates A transaction processing system (TPS) supports the monitoring, collection, storage, and


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
